How to classify text using the LinearClassification operator
Preconditions
With the composite Operator LinearClassification, available from https://github.com/IBMStreams/streamsx.nlp, you can find out which category an incoming text belongs to. As precondition, you need IBM Streams release 3.2 or newer and a previously calculated classification PKL model.
In practice, the model calculation is done in batch mode while the classification can run in real time on streaming input data. For convenience sample and test usage, the IBM Natual Language Processing (NLP) Toolkit also offers an operator for model creation: LinearClassificationModelBuilder.
Classification is one step in the native language processing pipe. Previous steps might be lemma transformation, removal of stop words and creation of n-grams. There are separate operators for those steps available in the IBM Streams NLP Toolkit. This article just concentrates on the LinearClassification operator.
Glossary
PKL - a serialized pickle file, dumped by using Python`s pickle module. It contains a serialized Python object structure.
NPY - a standard binary file format for persisting a single arbitrary NumPy array on disk.
NumPy - the fundamental package for scientific computing with Python.
Overview
In this example, the LinearClassificationModelBuilder operator calculates a model from training data. The LinearClassification operator applies this model to text from incoming tuple, which results in classification of this text. There are two output streams - one for classified data and another one for errors. In the example, we use only the classified data output stream and format it in two ways:
- The successful classifications with confidence values
- The same as 1 with the confidence values skipped
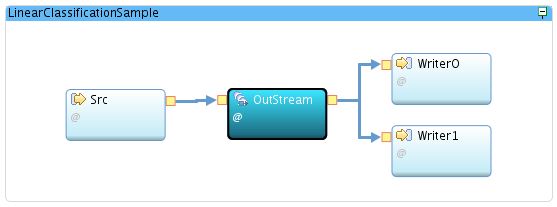
The Training Data
Model building needs training data. Training data contains already classified texts. In practice, you get better models the more training data in terms of volume and variety you have. For this sample, only a tiny set is used for the advantage of short run times and reproducible test results. It expects a comma-separated value (CSV) file with a text and the category of this text.
This is the first sentence,First
This is the second sentence,Second
This is something else,Else
The LinearClassificationModelBuilder Operator
To build a model, you can use the operator LinearClassificationModelBuilder. It needs two mandatory parameters:
- trainingFile - the training data file
- modelFilesDirectory - the directory for the model output
The operator calls an internal Python script to leverage TfidfVectorizer and LinearSVC from “Machine Learning in Python” (scikit-learn). You need at least Python 2.7 for the script to succeed. If you have multiple Python versions that are installed on your system, you can influence with the optional parameter pythonCommand what Python is used.

The Model
In result of the model building, you get several PKL and NPY files written to the specified model directory. Those files represent the model.

The Input
Now, you can classify new input data. The LinearClassification operator requires an input stream, which contains the data to classify in a stream attribute of type rstring (the documentAttribute).
In the sample input are two new strings.
ibm Streams first
something else
The LinearClassification Operator that uses the model
To classify new input, you use the LinearClassification operator. You call it with following attributes:
- documentAttribute - the attribute in the input tuple that contains the text for classification
- modelFilesDirectory - the directory that contains the model files
- outStreamType - the schema for the successful classification output. It needs to be the same as the output stream type of the LinearClassification operator.
The operator calls an internal Python script to leverage TfidfVectorizer and LinearSVC from “Machine Learning in Python” (scikit-learn). You need at least Python 2.7 for the script to succeed. If you have multiple Python versions that are installed on your system, you can influence with the optional parameter pythonCommand what Python is used.
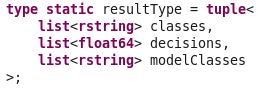
The Output
The LinearClassification operator delivers an output stream with up to three attributes:
- classes - the list of predicted categories (classification) (type list
) - decisions - the list of the appropriate numerical confidence values (type list
) Negative values mean that the original text would not fit to this category. Positive values mark a fit of the original text to a category. The confidence values represent the distance to the hyperplane. - modelClasses - the list of category names coming from the model (type list
) The index in the modelClasses list correlates to the index of the decisions list. This way it can support evaluation of the quality of predictions.
The remaining attributes in the output stream are automatically assigned from the input stream if attribute name and type match.
The sample formats the output in two different ways. One with the complete result that contains the determined categories (classes), the confidence values per category (decisions), the category names with the same index as the confidence values (modelClasses) and the original text. The other with only the determined categories and the original text.
["First"],[-0.32845056,0.14259748,-0.4873244],["Else","First","Second"],ibm Streams first
["Else"],[0.40863002,-0.58213577,-0.58213406],["Else","First","Second"],something else
In the sample output the original text “ibm Streams first” fits to trained model category “First” with distance to hyperplane value 0.14259748. The other model categories (“Else” and “Second”) do not fit with negative distance to hyperplane values.
Original text “something else” fits to class “Else” with distance to hyperplane value 0.40863002.
How to calculate the model outside Streams?
There are Python scripts that do the work behind the operators LinearClassificationModelBuilder and LinearClassification. The script LinearClassificationModelBuilder.py can create the model for example, in Spark also.
It is important to ensure that the Python scripts that are used in the model building (LinearClassificationModelBuilder.py) and in the classification (LinearClassification.py) fit together in terms of algorithm and file names. Only the model directory is variable.
Summary
The LinearClassification operator allows to classify new incoming text according to a trained model. If you wish to replace the model with a newer one, you need to restart the instance at the moment. In order to consider new models at run time, the operator would need enhancement with a control port to trigger the read of a new model.